রিটেলে RFID (রেডিও ফ্রিকোয়েন্সি আইডেন্টিফিকেশন) প্রযুক্তির ব্যবহার ২০০০ সালে শুরু হয়েছিল যখন ওয়ালমার্ট সাপ্লাই চেইন ম্যানেজমেন্টে এটির ব্যবহার প্রচলন করে। এটি রিটেল শিল্পের জন্য একটি পরিবর্তনমূলক যাত্রার শুরু চিহ্নিত করেছিল। ২০১০ সালে, ডেকাথলন একটি RFID উপ-কোম্পানি প্রতিষ্ঠা করে, অন্যদিকে জারার মাতৃকোম্পানি ইন্ডিটেক্স ২০১৪ সালে এই প্রযুক্তিকে তাদের সকল ব্র্যান্ডে গ্রহণ করে। তখন থেকে, RFID জুতা এবং সুপারমার্কেট রিটেল খন্ডে ব্যাপকভাবে ব্যবহৃত হয়ে আসছে। ম্যাকিন্সির একটি সর্বেক্ষণ অনুযায়ী, ইউরোপ এবং মার্কিন যুক্তরাষ্ট্রের ৭৩% রিটেলার এখনও বা ভবিষ্যতে RFID সমাধান ব্যবহার করছে বা করতে চায়, যা এর দ্রুত বৃদ্ধির প্রতিফলন। প্রযুক্তির দিক থেকে, RFID এখন পরিপক্ব হয়েছে, বিশেষ করে ইউরোপ এবং উত্তর আমেরিকা মতো উন্নয়নশীল বাজারে, যেখানে এটি আধুনিক রিটেল অপারেশনের একটি মৌলিক অংশ হয়ে উঠেছে।
আজ, RFID প্রযুক্তি বিভিন্ন শিল্পের উপর প্রয়োগ করা হয়েছে এবং এটি একটি পাকা সমাধান হয়ে উঠেছে। এই নিবন্ধটি এর উন্নয়ন, বর্তমান অ্যাপ্লিকেশন, মূল ট্যাগ ধরণ এবং জুতা এবং সুপারমার্কেট রিটেল বাজারে এর মূল্যের উপর আলোকপাত করে, এর অতীত, বর্তমান এবং ভবিষ্যতের দিকে দৃষ্টি নিবদ্ধ করে।

জুতা, পোশাক এবং রিটেলের বর্তমান বাজার অবস্থা
জুতা, পোশাক এবং রিটেল খন্ডটি তিনটি মূল শ্রেণীতে বিভক্ত করা যেতে পারে: পোশাক এবং অ্যাক্সেসোরি, হার্ডওয়্যার পণ্য এবং খাদ্য এবং ওষুধ। নিচে এই অঞ্চলে RFID ট্যাগের অ্যাপ্লিকেশনের একটি সংক্ষিপ্ত বিবরণ দেওয়া হল।
১.১ পোশাক এবং অ্যাক্সেসোরি
চাদর এবং অ্যাক্সেসোরি খন্ডটি ইতিমধ্যে RFID অ্যাপ্লিকেশনের জন্য পরিপক্ব ক্ষেত্র। যুক্তরাষ্ট্র এবং ইউরোপ জैसी উন্নয়নশীল দেশগুলিতে, RFID-এর ব্যবহার ব্যাপক। তবে চীন জৈসা উন্নয়নশীল দেশে, যেখানে শ্রম খরচ বিশেষভাবে কম, হাতে-করা বা QR কোড-ভিত্তিক ইনভেন্টরি ম্যানেজমেন্ট এখনও প্রধান পদ্ধতি। AIOT Research Institute-এর তথ্য অনুযায়ী, Adidas, Nike, Uniqlo, MUJI, H&M এবং UR জৈসা ফাস্ট-ফ্যাশন এবং স্পোর্টসওয়্যার ব্র্যান্ডগুলি হলো RFID গ্রহণের সবচেয়ে সক্রিয়। এছাড়াও, নতুন ব্র্যান্ড এবং স্বাধীন ডিজাইনাররা তাদের পণ্য ম্যানেজ করতে RFID ট্যাগ ব্যবহার শুরু করেছে।
১.২ হার্ডওয়্যার পণ্য
প্রথম এবং দ্বিতীয়-স্তরের শহরে, মূল্য প্রদর্শনের জন্য ইলেকট্রনিক শেলফ লেবেল (ESL) ব্যবহার একটি উল্লেখযোগ্য প্রবণতা হিসেবে উদয় হচ্ছে। তবে, RFID এসএল-এর সাথে অনুকূল হতে পারে যা ইনভেন্টরি রোটেশনের দক্ষতা বাড়াতে সাহায্য করে। যদিও এই অঞ্চলটি এখনও ব্যাপকভাবে গৃহীত হয়নি, এটি অনেক আরএফআইডি শিল্পজ্ঞের জন্য একটি ফোকাস। 3C খন্ডে, বিশেষত স্মার্টফোনের জন্য, আশা করা হচ্ছে যে এনএফসি (আরএফআইডির একটি উপসেট) ব্যবস্থাপনার জন্য ব্যবহৃত হবে, এবং কিছু দেশ ইতিমধ্যে এর বাস্তবায়ন পরীক্ষা করছে।
১.৩ খাদ্য এবং ঔষধ
কিছু আন্তর্জাতিক ব্র্যান্ড খাদ্য এবং ঔষধ শিল্পে আরএফআইডি ট্যাগ ব্যবহারের পরীক্ষা শুরু করেছে। রেড বুল, রাইট এড এবং সান ডানিয়েলের মতো কোম্পানিগুলি কিছু পণ্যের জন্য আরএফআইডি ট্যাগ বিতরণ শুরু করেছে। এই খন্ডে, আরএফআইডি শুধুমাত্র দ্রুত ইনভেন্টরি পরীক্ষা এবং আইটেম ট্র্যাকিং সহায়তা করে না, বরং মিথ্যা পণ্য রোধ, ট্রেসাবিলিটি এবং মেয়াদের ব্যবস্থাপনায়ও গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে।
কাগজের উপর আधারিত আরএফআইডি ট্যাগ
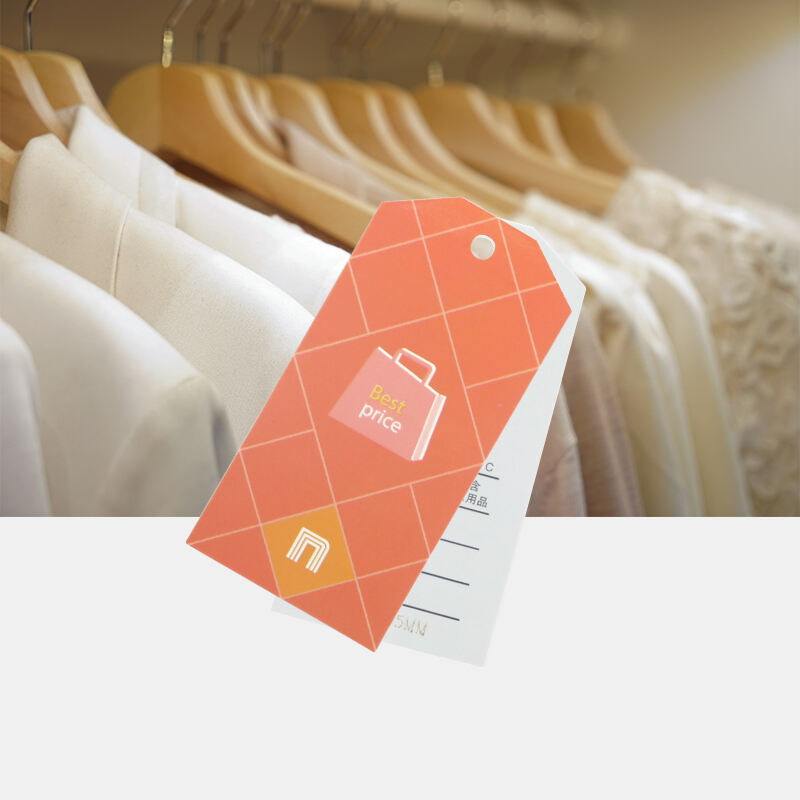
কাগজের উপর ভিত্তি করে আরএফআইডি ট্যাগগুলি পোশাক শিল্পে সবচেয়ে বেশি ব্যবহৃত হয়। এগুলি দুটি রূপে পাওয়া যায়: মোটা ইনলেয় এবং শুকনো ইনলেয়, যেখানে মোটা ইনলেয় বেশি জনপ্রিয়। এই ট্যাগগুলি পণ্যের হ্যাঙ্কট্যাগে সরাসরি একত্রিত করা যেতে পারে, যা অতিরিক্ত উৎপাদন ধাপ ছাড়াই সহজে পরিবর্তন করতে দেয়। কিছু রিটেইলার এনএফসি বা অন্যান্য আরএফআইডি পণ্য ব্যবহার করে, পণ্যের শীর্ষ থেকে নিচে পর্যন্ত পণ্য পরিচালনা করতে ট্যাগ সরাসরি আইটেমে যুক্ত করে। তবে, কাগজের উপর ভিত্তি করে ট্যাগগুলি উৎপাদনের সময় হ্যাঙ্কট্যাগ বা পণ্যের সাথে যোগ করার জন্য একটি অতিরিক্ত ধাপ প্রয়োজন।

হ্যাঙ্কট্যাগ আরএফআইডি লেবেল
হ্যাঙ্কট্যাগ আরএফআইডি লেবেল পোশাক রিটেইল খন্ডের দ্বিতীয় সবচেয়ে সাধারণ রূপ। এগুলি প্রধানত পোশাক, জুতা এবং কিছু মহিলাদের হ্যান্ডব্যাগের জন্য ব্যবহৃত হয়। হ্যাঙ্কট্যাগ লেবেলের ক্ষেত্রে, শুধুমাত্র ট্যাগ ডেটা সিনক্রোনাইজ করা প্রয়োজন, যা অতিরিক্ত উৎপাদন প্রক্রিয়ার প্রয়োজন বাদ দেয়।

উইভন আরএফআইডি লেবেল
বুনা রেডিও-ফ্রিকোয়েন্সি আইডি (RFID) লেবেল মূলত ধোঁয়ার পণ্যে, যেমন হোটেল এবং হাসপাতালে, ব্যবহৃত হয়। নিয়মিত ধোয়ার প্রয়োজনীয় কোটন পণ্যের জন্য কিছু কোম্পানি ফেব্রিকে RFID লেবেল সিউ করে পণ্য এবং ঘরের তথ্য ট্র্যাক করতে ব্যবহার করে। উল্লেখ্য যে, জারা এখন তাদের বিদেশী দোকানে বুনা লেবেল ব্যবহারের পরীক্ষা শুরু করেছে, ঐতিহ্যবাহী হ্যাঙ্গট্যাগ প্রতিস্থাপনের জন্য, যা এই ধরনের লেবেলের জন্য ভবিষ্যতে বৃদ্ধির সূচনা করতে পারে।

অ্যান্টি-মেটাল আরএফআইডি ট্যাগ
অ্যান্টি-মেটাল RFID ট্যাগ পোশাক শিল্পে খুব কমই ব্যবহৃত হয়, যেমন কিছু চামু পোশাক বা ধাতু উপাদানসহ পোশাকে। তবে, তারা বেশিরভাগ সময় ড্রিংক শিল্পে ব্যবহৃত হয়, যেখানে ধাতু ক্যান বা বোতলে NFC ট্যাগ অ্যাপ্লাই করা হয়।
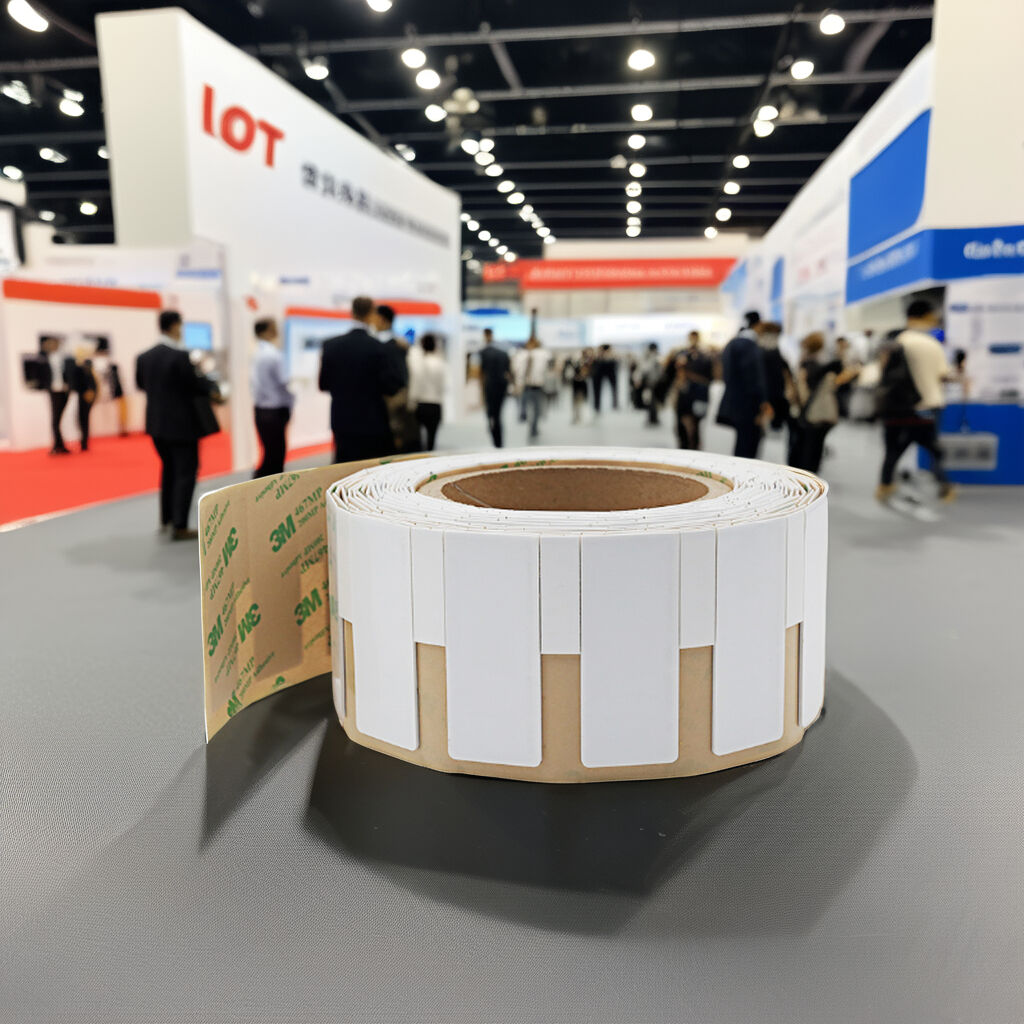
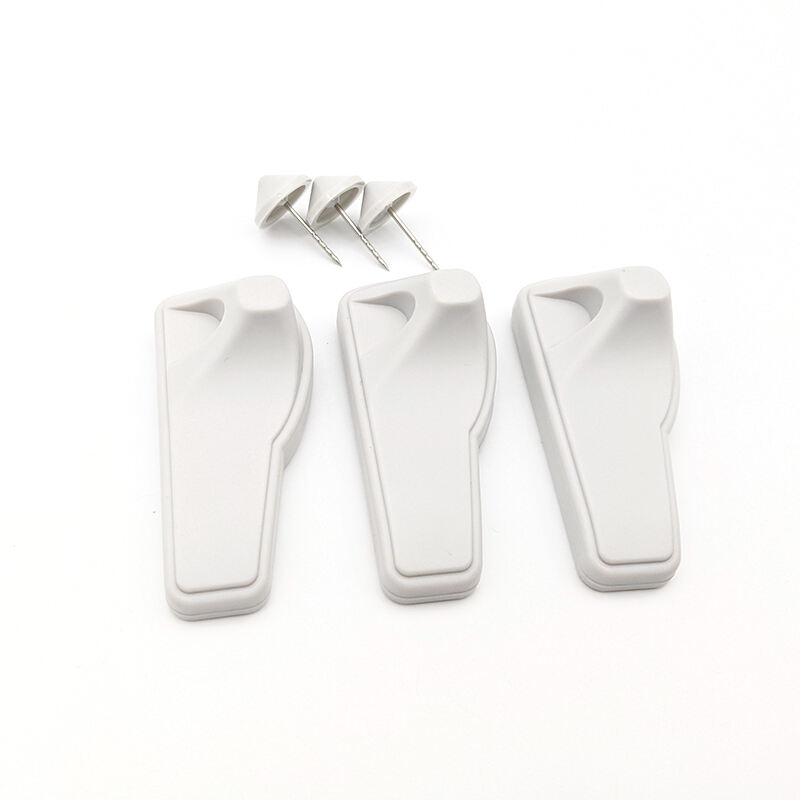
হার্ড-শেল RFID ট্যাগ
হার্ড-শেল RFID ট্যাগ ঐতিহ্যবাহী EAS (ইলেকট্রনিক আর্টিকেল সারভেলেন্স) এবং RFID প্রযুক্তি একত্রিত করে বহুমুখী কাজের সুযোগ দেয়। সাম্প্রতিককালে, কিছু প্রস্তুতকারক একমাত্র RFID-এর ব্যবহার পরীক্ষা করেছে যা EAS-কে প্রতিস্থাপন করবে, চুরি রোধ এবং পরিচালনা কাজের অনুমতি দেওয়ার জন্য।

রিটেল পরিস্থিতিতে, RFID ট্যাগ ইনভেন্টরি ম্যানেজমেন্ট, স্মার্ট ফিটিং রুম, স্টক অবস্থান নির্ধারণ, দ্রুত চেকআউট, আউট-অফ-স্টক সংকেত, চুরি রোধ, গ্রাহক প্রবাহ বিশ্লেষণ, কাউন্টারফিটিং রোধ এবং সাপ্লাই চেইন ম্যানেজমেন্ট এমন কাজগুলোকে সম্ভব করে এবং এর মাধ্যমে অপারেশনাল দক্ষতা বাড়ানো হয়। অনেক পোশাক ব্র্যান্ড অকার্যকর সাপ্লাই চেইন, বढ়তি শ্রম খরচ এবং অস্পষ্ট বাজার প্রবণতা এমন চ্যালেঞ্জের মুখোমুখি হয়। ঐচ্ছিক বারকোড ভিত্তিক ম্যানেজমেন্ট সিস্টেম সময়সাপেক্ষ, শ্রম-ভর্তি এবং স্থান-অপদার্থ। তুলনায়, UHF RFID প্রযুক্তি এই সমস্যাগুলোকে সমাধান করে প্রস্তুতি, গোদাম ম্যানেজমেন্ট, ব্র্যান্ড ম্যানেজমেন্ট এবং চ্যানেল ম্যানেজমেন্ট একটি সহজ পদ্ধতি আনে এবং পোশাক শিল্পে বিশাল সুবিধা আনে।
Xinye RFID : ফুটওয়্যার এবং সুপারমার্কেট রিটেলে RFID শক্তিশালী করে
গুয়ানড়োং সিনই ইন্টেলিজেন্ট লেবেল কো, লিমিটেড। RFID সমাধানের এক নেতা, জুতা এবং সুপারমার্কেট রিটেল বাজারে প্রভাবশালী উদ্ভাবন চালু করছে। উচ্চ-পারফরমেন্স RFID ট্যাগ এবং ব্যবহারভিত্তিক সিস্টেমের উপর ফোকাস দিয়ে, সিনই রিটেলারদের অপারেশনাল চ্যালেঞ্জ অতিক্রম এবং ডিজিটাল রূপান্তর সাধনের ক্ষমতা দান করে। তাদের পণ্য শ্রেণীবিভাগে আছে কাগজের ট্যাগ, বুনো লেবেল এবং হার্ড-শেল ট্যাগ, যা পোশাক, জুতা এবং গ্রোসারি চেইনের বিশেষ প্রয়োজনের জন্য ডিজাইন করা হয়েছে।
Xinyerfid-এর সমাধান স্টক ব্যবস্থাপনা সহজ করে, শ্রম খরচ কমায় এবং দ্রুত স্টক গণনা এবং স্মার্ট চেকআউট সিস্টেমের মতো বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলির মাধ্যমে গ্রাহকদের অভিজ্ঞতা উন্নয়ন করে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, তাদের UHF RFID ট্যাগ সরবরাহ চেইনের মধ্যে বাস্তব-সময়ে ট্র্যাকিং সম্ভব করে, যা ফাস্ট-ফ্যাশন রিটেলার এবং সুপারমার্কেটের মতো ব্র্যান্ডগুলি স্টক স্তর অপটিমাইজ এবং ক্ষতি রোধ করতে সাহায্য করে। এছাড়াও, সিনই শিল্প সহযোগীদের সাথে কাজ করে এবং IoT এবং AI মতো নতুন প্রযুক্তি সঙ্গে RFID এর একাত্মকরণ করে, যা স্মার্টার রিটেল ইকোসিস্টেমের পথ প্রসারিত করে।
আগের দিকে তাকিয়ে, Xinye RFID বিশ্বব্যাপী RFID গ্রহণ বাড়ানোর জন্য সমर্থিত, বিশেষত চীনের মতো উন্নয়নশীল বাজারে, যেখানে খরচজনিত সমাধান হাতেকাটা প্রক্রিয়া এবং ইউটোমেশনের ফাঁক ভরতে পারে। স্কেলেবল, নির্ভরশীল এবং আফordable RFID প্রযুক্তি প্রদান করে থাকায়, Xinye RFID রিটেলের দক্ষতা এবং লাভজনকতার ভবিষ্যৎ আকার করতে প্রস্তুত।